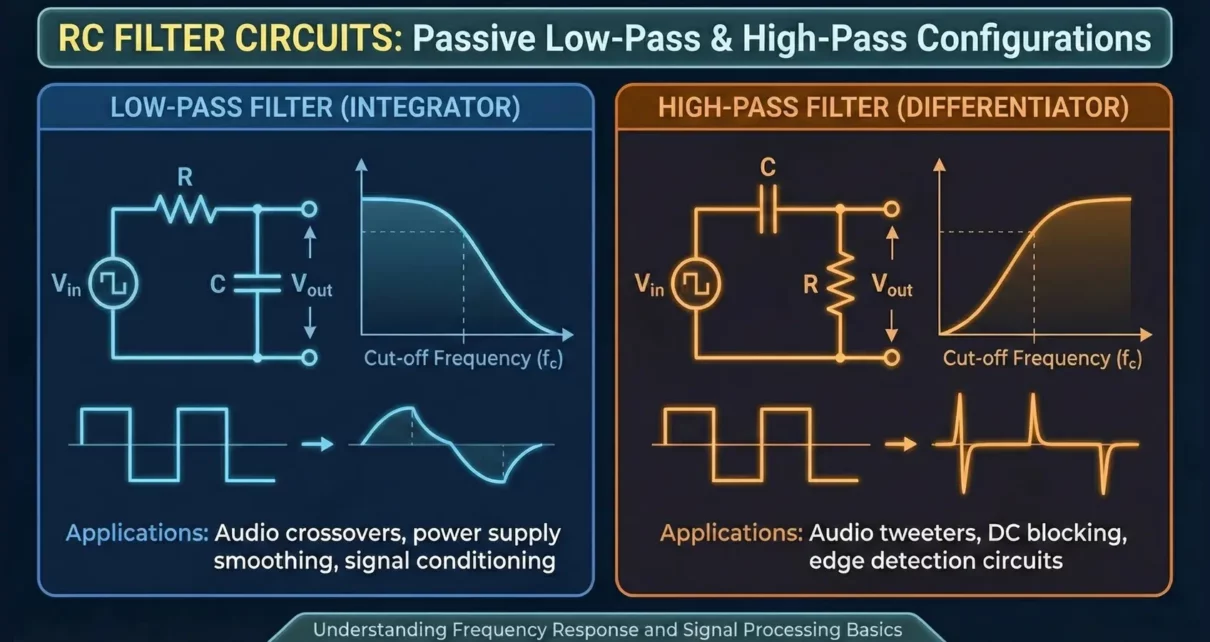
RC filters are the most fundamental signal-processing circuits in electronics. It uses a combination of a resistor (R) and a capacitor (C) to selectively allow or suppress signals based on their frequency. Despite its simplicity, the RC filter plays a crucial role in almost every electronic system, from basic audio amplifiers to complex communication and […]
How Dryer Repair Experts Can Extend Your Appliance’s Life
When your laundry piles up and the dryer suddenly stops working, the first people you’ll think of calling are dryer repair experts Clermont, FL. These professionals don’t just fix the issue – they help prevent bigger, costlier breakdowns down the road. A well-maintained dryer can last years longer, saving you money and frustration. The Importance […]
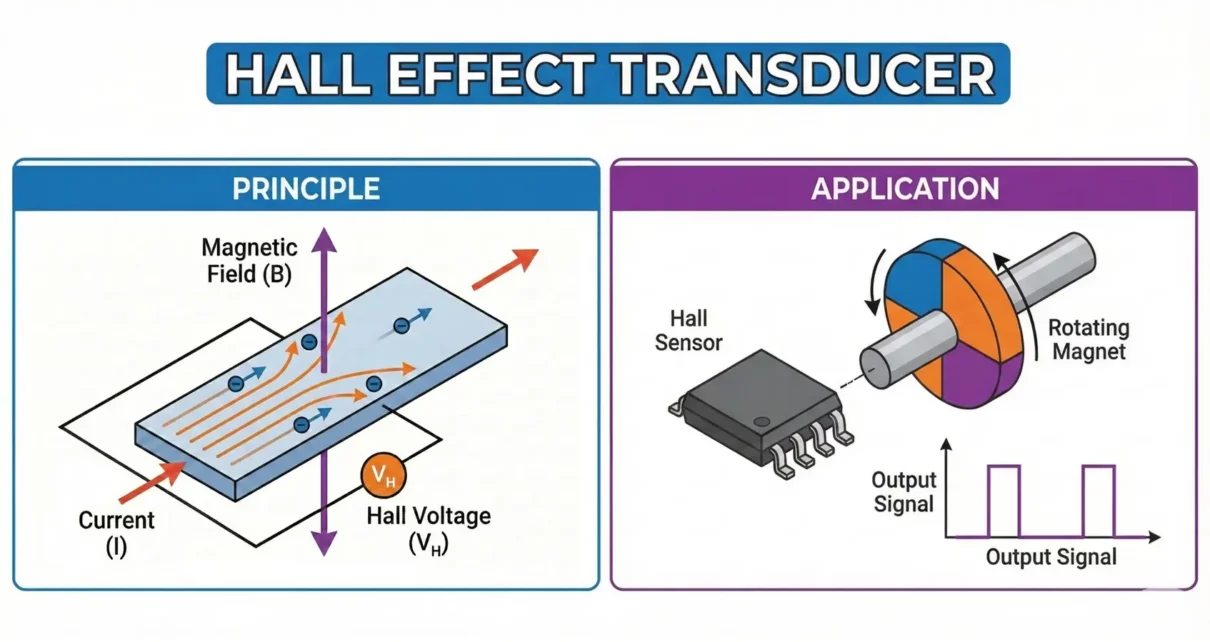
Hall Effect Transducer Construction, Working and Applications
A Hall effect transducer is a sensor that detects a magnetic field and converts it into a proportional electrical signal using the Hall effect phenomenon. It is widely used for current sensing, position sensing, speed detection, proximity sensing, and magnetic field measurement in industrial, automotive, and consumer electronic systems. Unlike conventional mechanical or contact-based sensors, […]
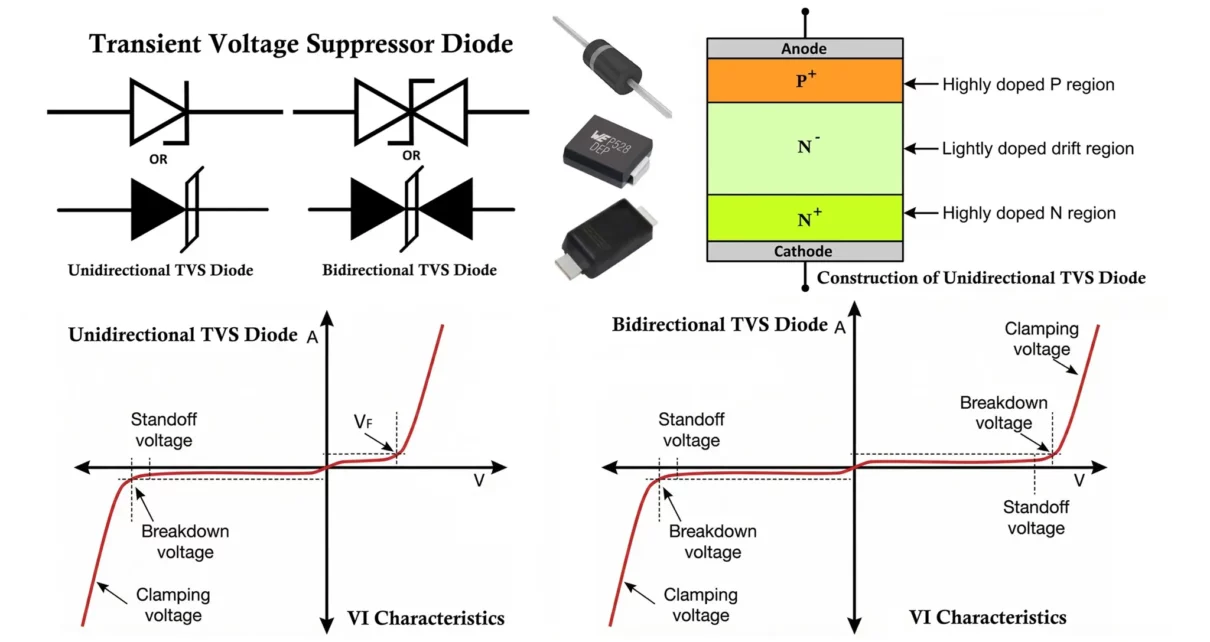
TVS Diode: Symbol, Construction, Working, Types and Applications
A TVS (Transient Voltage Suppression) diode is a specialized semiconductor device used to protect electronic circuits from high-voltage transients such as electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and switching spikes. It responds extremely fast and clamps overvoltage to a safe level before they damage sensitive components. Modern electronic systems are highly sensitive to voltage spikes caused […]
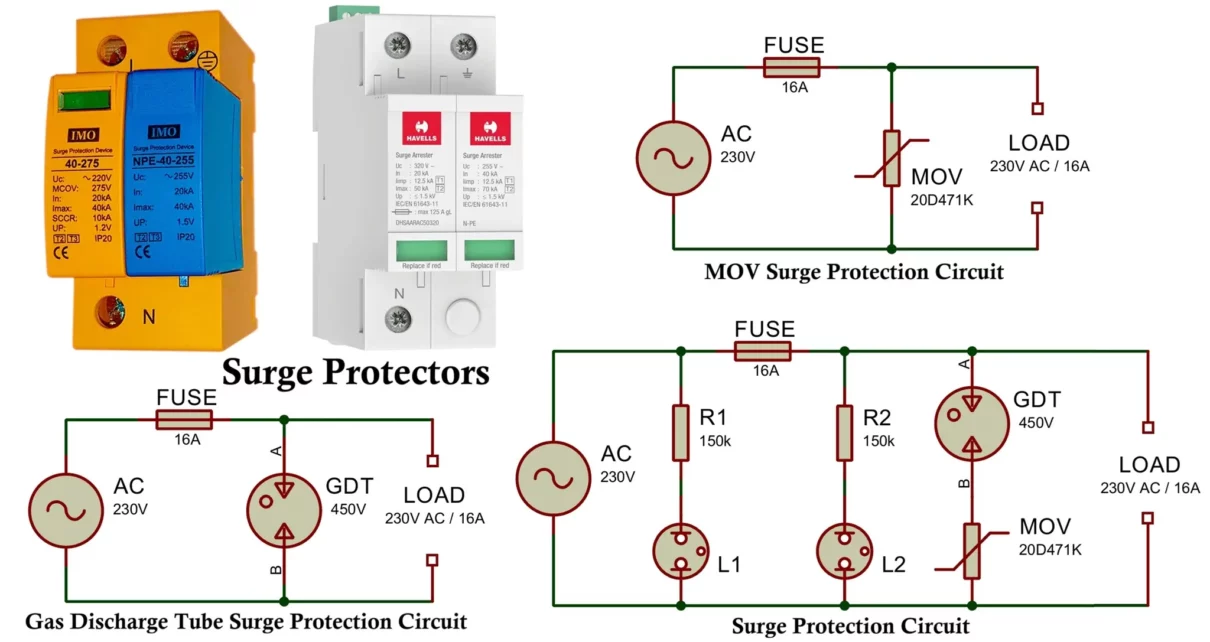
Surge Protector Circuit Diagram, Working, Types and Applications
A surge protector is an electronic protection device designed to safeguard electrical and electronic equipment from voltage surges (transient overvoltage). A voltage surge is a sudden and short-duration spike in voltage that exceeds the normal operating voltage of a system. These surges may last from a few nanoseconds to milliseconds but can reach several kilovolts […]
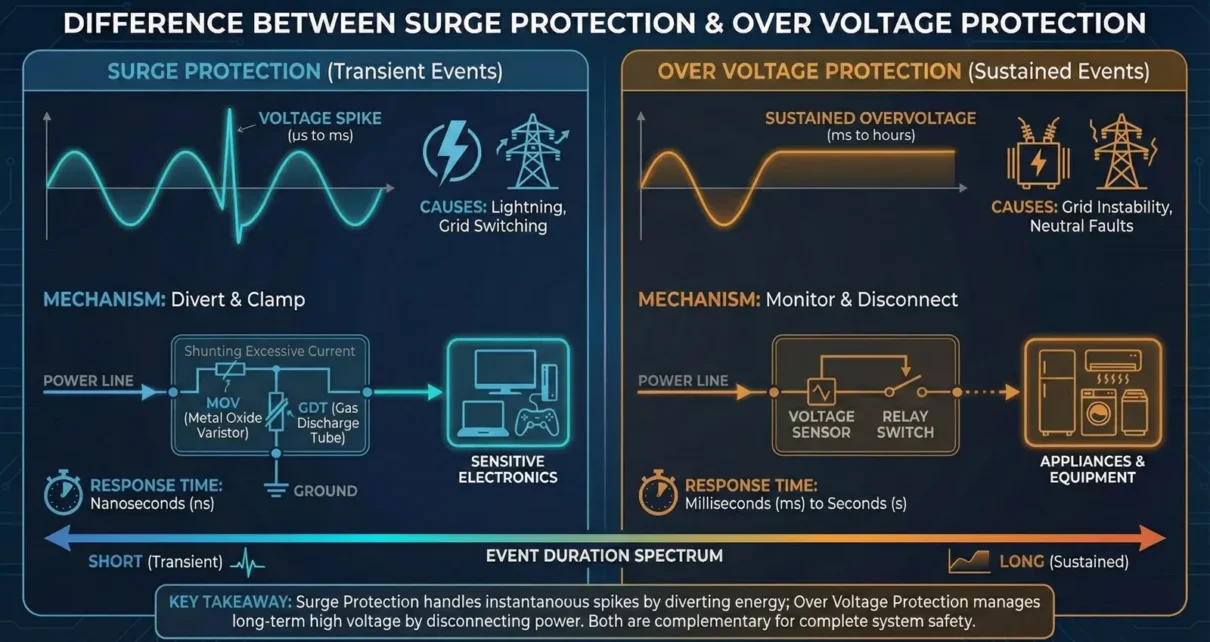
Difference Between Surge Protection and Over Voltage Protection
Understanding the difference between Surge Protection and Over Voltage Protection is essential for designing robust electronic systems, selecting the right protective components, and complying with safety and EMC standards. Modern electronic and electrical systems are increasingly sensitive to abnormal voltage conditions. With the widespread use of microcontrollers, SMPS power supplies, communication modules, and semiconductor devices, […]