Scaling of MOSFET means, the Reduction of scales from something, Hey! Friends let us first understand what is the basic idea behind the scaling of MOSFET? Scaling is one of the best ways to increase the performance of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFET). In scaling we reduced some critical parameters of the MOSFET, to obtain the desired operational characteristics. Further in this blog, we are going to study the proper definition of Scaling, and what are the scaling factors by which scaling of mos Transistors can be done. The Scaling Factors such as Gate length, Voltage, and Channel Width. How Scaling of MOS transistor Affects the Drain Current. Also, we are going to discuss in detail what are the different types of scaling.
By using this method of scaling semiconductor companies like Intel or AMD can add more transistors on the same size of a silicon wafer. This is why performance, speed, and core count in CPU increases every year.
Definition of MOSFET Scaling-:
Scaling of a MOS transistor means reducing the critical parameter of the device in accordance with a given criterion in order to improve some performance features such as Speed, Application, Power Dissipation, and so on while keeping the basic operational characteristics unchanged.
Advantages of scaling in MOSFET:
- Packaging Density: The packing density of the device improves as a result of scaling hence we can fit more transistors in the same space as before.
- Size Chip: As we can pack more number of transistors in the same space hence, we can decrease the overall area of the chip.
- Multifunction of Chip: As transistor size is reduced, we can make multifunctional chips by reducing the area of chips.
Types of Scaling in MOSFETs-:
Scaling can be classified into three categories, which are detailed below.
- Constant Field Scaling or Full Scaling.
- Constant Voltage Scaling.
- Lateral Scaling.
Constant Field Scaling or Full Scaling-:
In this, all the parameter of the MOSFET is scaled to understand it in a better way we will consider a case, suppose the scaling factor is “S” who’s values greater than 1 (S>1) now consider all the parameters of MOSFET is scaled by scaling factor “S” then it’s all parameter will get changed to a new value.
For example, if the original gate length is “L” then after scaling it will become L’ = L/S
In a similar way, all parameters of the MOSFET will get changed to their new value hence this type of scaling is known as the Full Scaling.
Constant Voltage Scaling-:
In this only, the physical parameters of the MOSFET are Scaled-down such as the Gate length of the MOSFET is decreased, and this result In a Short Channel Effect which will directly affect the Drain Current, therefore the drain Current is Inversely proportional to gate length. And electrical Parameters are kept constant, such as the terminal voltage of the MOSFET is kept constant.

Lateral Scaling-:
In this type of scaling only the width of the gate channel is scaled. It’s commonly called a gate shrink. This type of scaling is used only in specific applications. the disadvantage associate with this type is the high electric field through the channel and hence it also causes a short channel effect.

Scaling of MOSFET
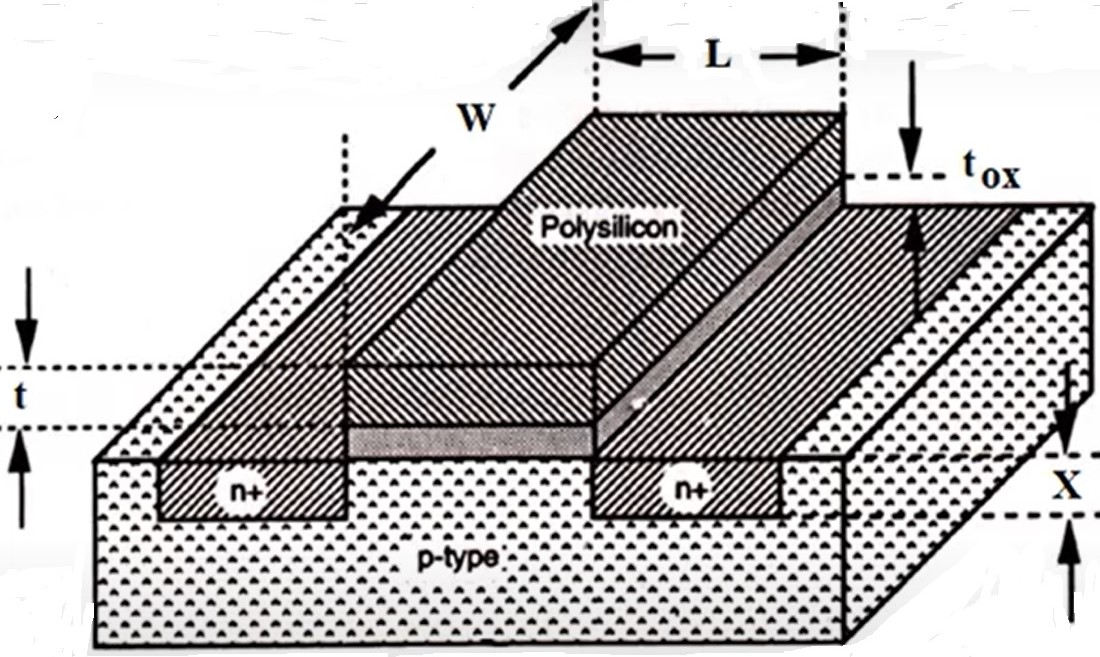

This blog is informative.The one who don’t know about these topics can easily understand what’s it.