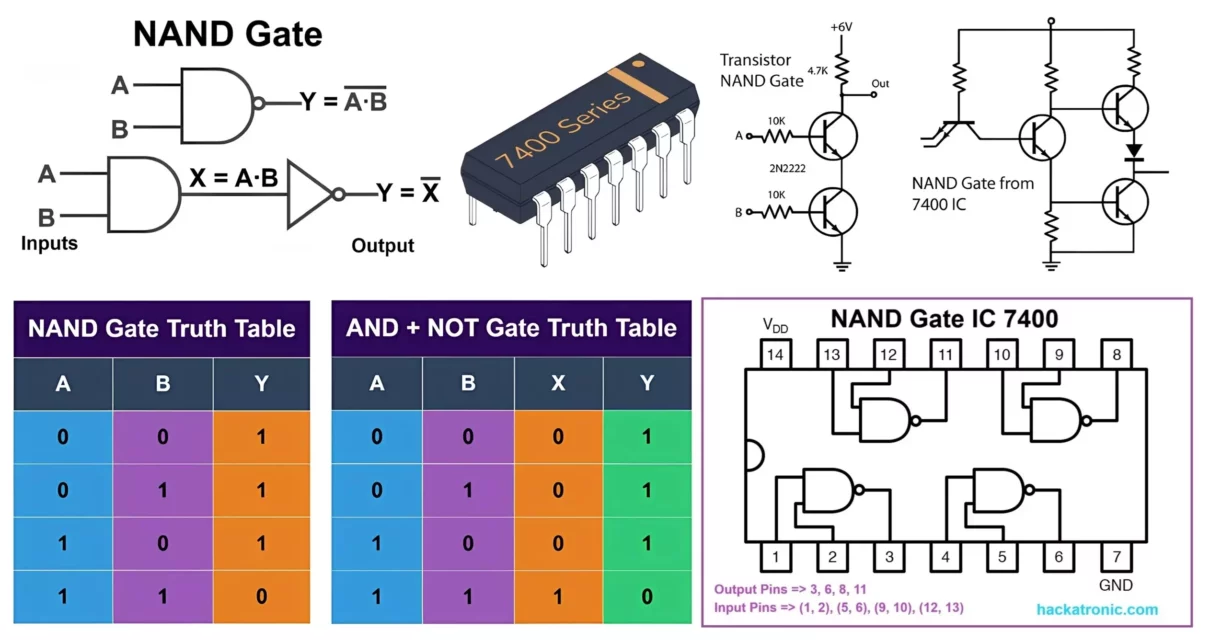
Explore Universal NAND Gate from its truth table to its IC pin diagram, delve into transistor-based logic circuit construction and working, and discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and various applications of the NAND gate. Just as the NOR gate combines the OR and NOT functions to provide an inverted output when all inputs are low, the […]
Tag: Digital Electronics
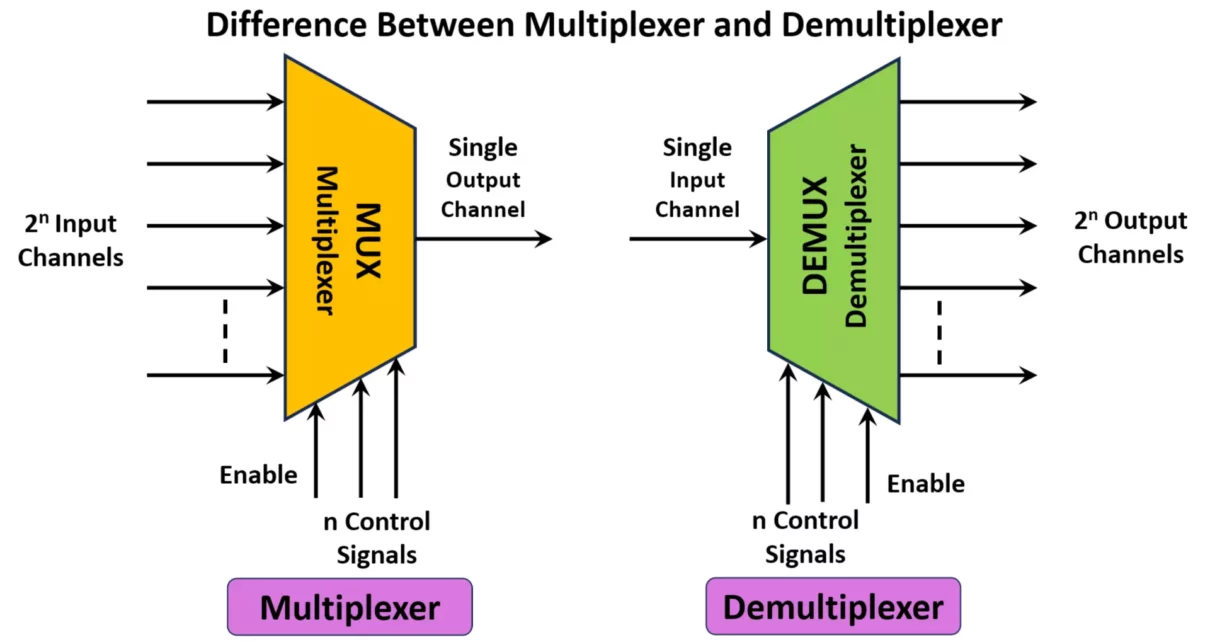
Difference Between Multiplexer and Demultiplexer with Types
Multiplexers (MUX) and Demultiplexers (DEMUX) are essential combinational logic circuits used in digital electronics for data transmission and communication systems. They play a crucial role in efficiently handling multiple signals by optimizing the usage of data lines, reducing hardware complexity, and enhancing the efficiency of data processing units. Let’s explore the difference between multiplexer and […]
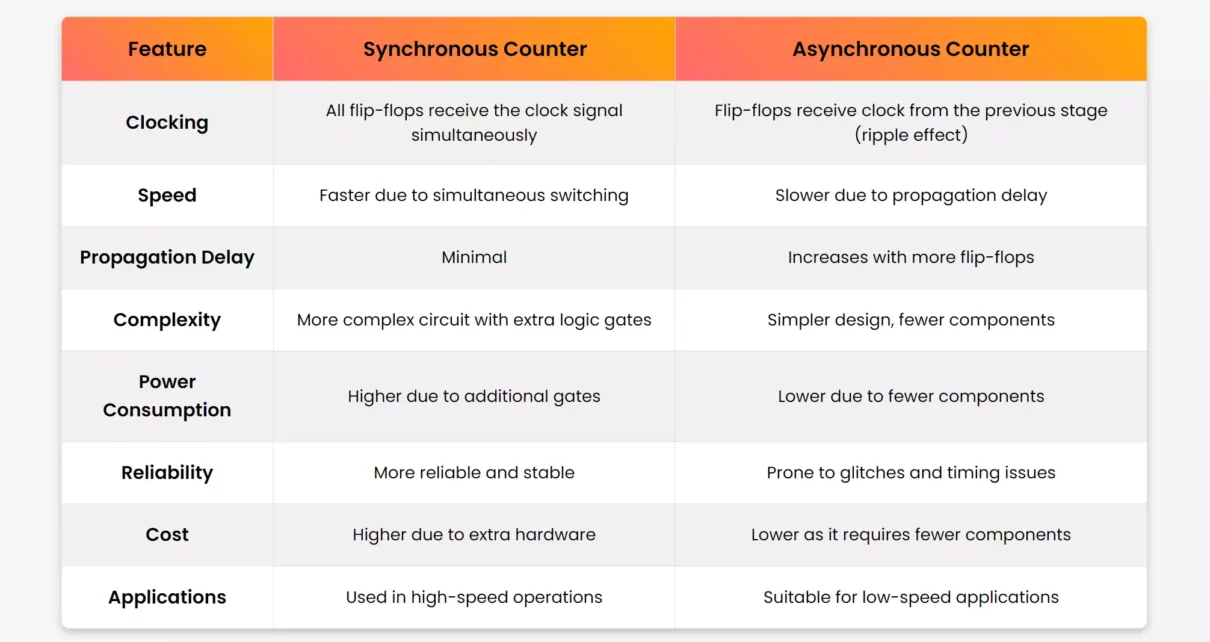
Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters
Counters are fundamental digital circuits used in sequential logic for counting purposes. They are broadly classified into two types: Synchronous Counters and Asynchronous Counters. Understanding the difference between synchronous and asynchronous counters helps in choosing the right type for specific applications in digital electronics. These counters play a crucial role in modern digital systems, ranging […]
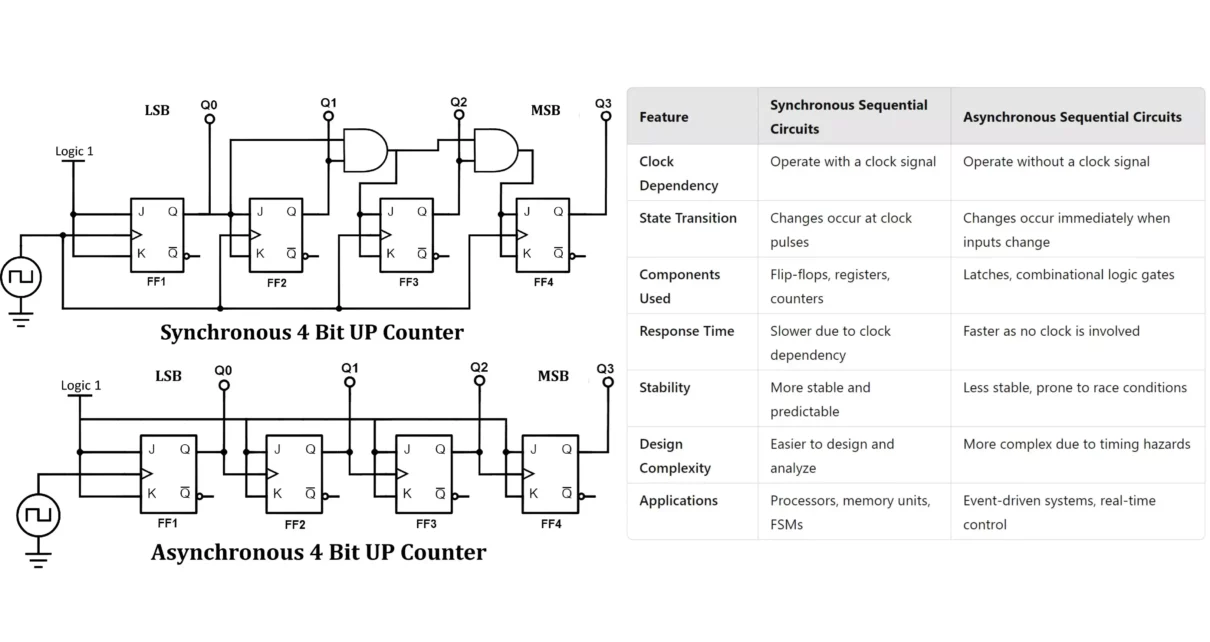
Difference Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
Sequential circuits are of two types: Synchronous Sequential Circuits and Asynchronous Sequential Circuits. The difference between them is that synchronous circuits use a clock signal to control state changes, making them more predictable and easier to design. In contrast, asynchronous circuits do not rely on a clock and change states based on input signals, which […]
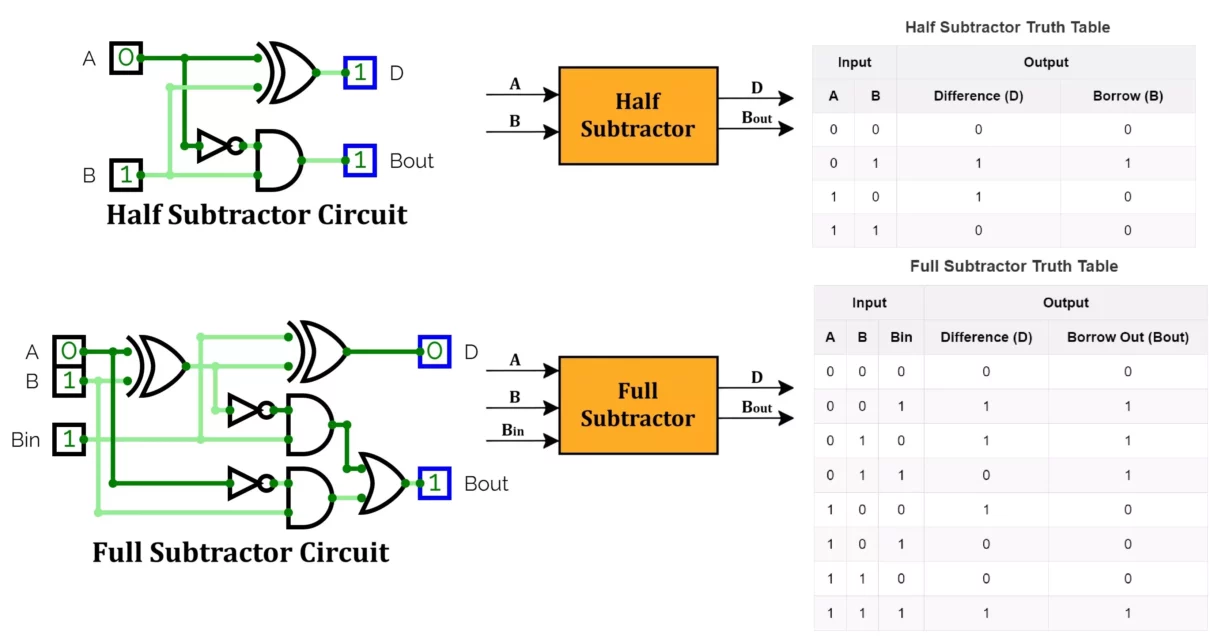
Half Subtractor and Full Subtractor: Circuit, Truth Table & Equation
In this article, we will discuss Half Subtractor Circuit and Full Subtractor Circuit with their working principle, truth table, equations, Karnaugh maps (K-map) and applications. Subtraction is a fundamental arithmetic operation in digital electronics, and logic circuits efficiently implement it. A subtractor is a combinational circuit that performs binary number subtraction in digital systems. These […]
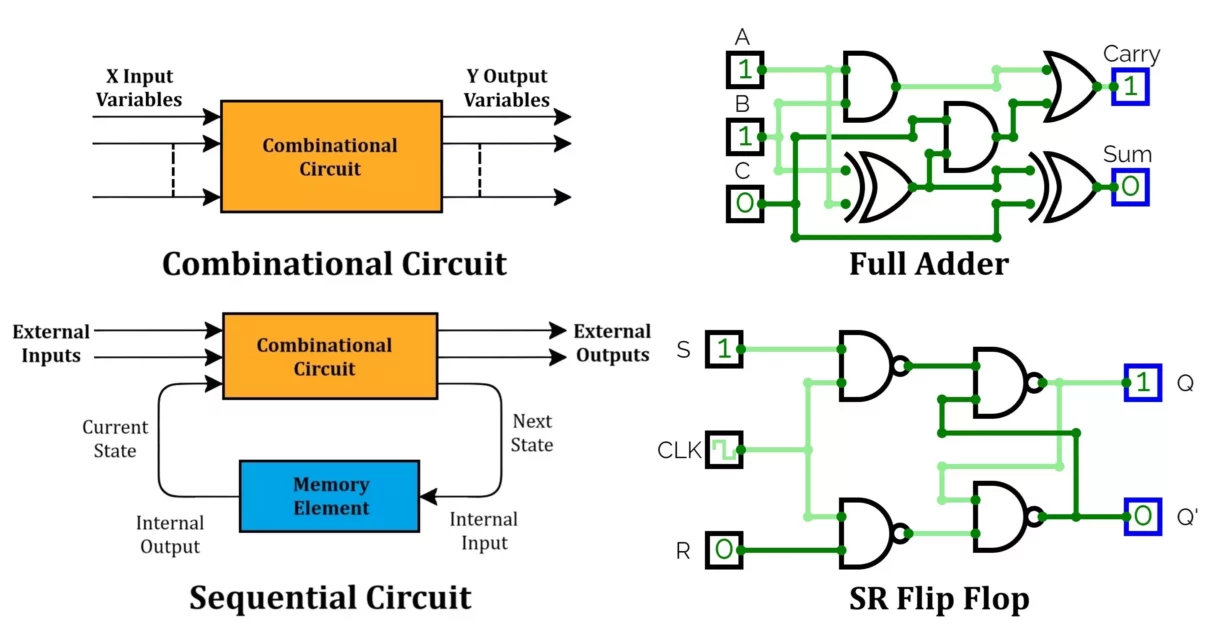
Difference Between Combinational and Sequential Circuits
Digital circuits are broadly classified into two types: Combinational Circuits and Sequential Circuits. These circuits are fundamental building blocks in digital electronics and play a significant role in designing various digital systems. This article explores the differences between these two types of circuits in detail, discussing their characteristics, examples, advantages, disadvantages, applications along with some […]