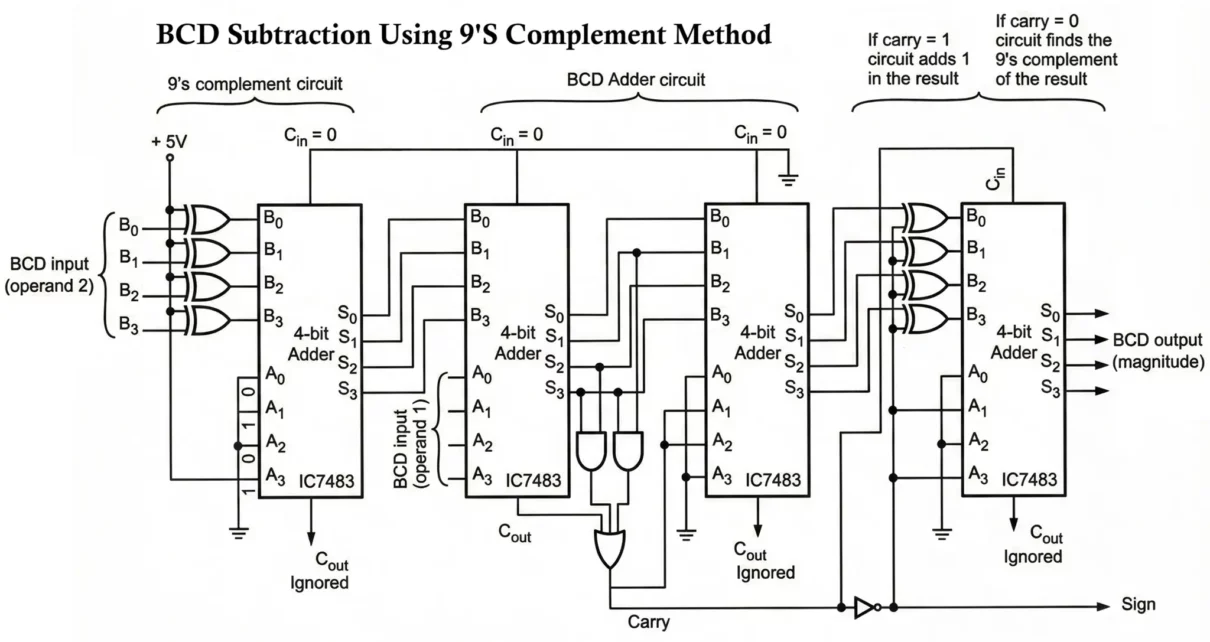
While a BCD adder performs decimal addition using binary hardware with correction logic, a BCD subtractor performs the subtraction of one BCD number from another and produces a valid BCD result. This requires additional logic because simple binary subtraction does not automatically produce valid BCD outputs. Digital systems frequently need to perform arithmetic operations such […]
Logic Gates
BCD Adder Circuit Diagram, Truth Table, Working and Applications
Let’s explore the BCD Adder Circuit and learn how it adds decimal digits using Binary Coded Decimal (BCD), a digital coding system in which each decimal digit is represented using a 4-bit binary number. BCD arithmetic is widely used in digital systems where calculations must remain in decimal form, such as calculators, clocks, and display-based […]
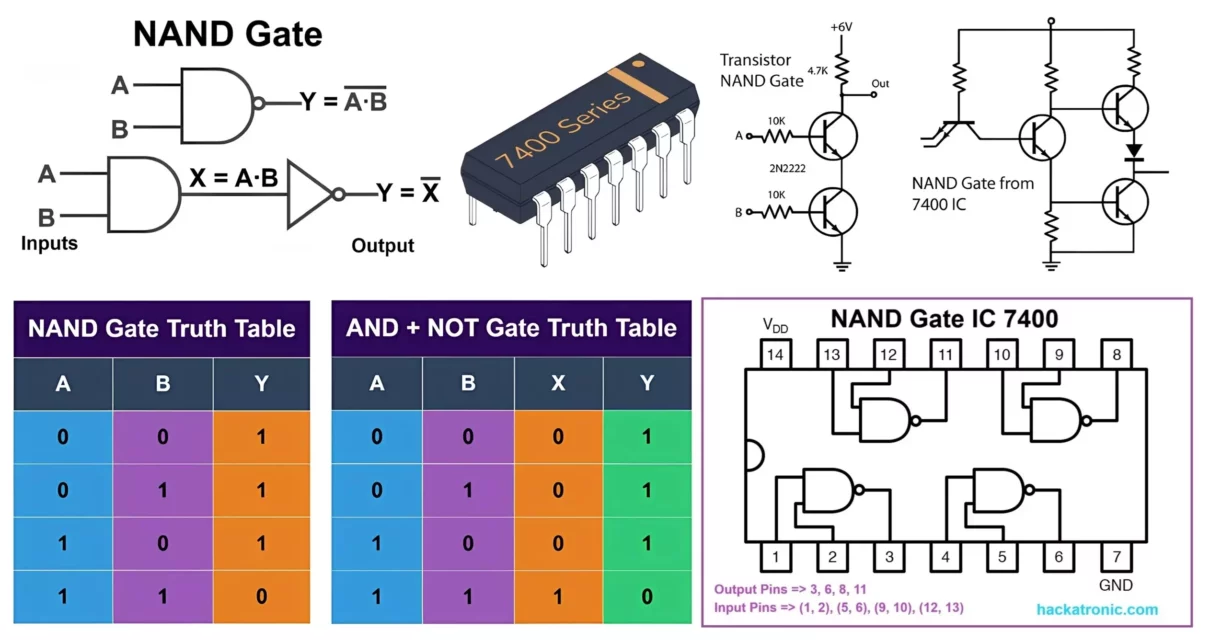
Universal NAND Gate Truth Table, Logic Circuit & IC 7400 Pin Diagram
Explore Universal NAND Gate from its truth table to its IC pin diagram, delve into transistor-based logic circuit construction and working, and discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and various applications of the NAND gate. Just as the NOR gate combines the OR and NOT functions to provide an inverted output when all inputs are low, the […]
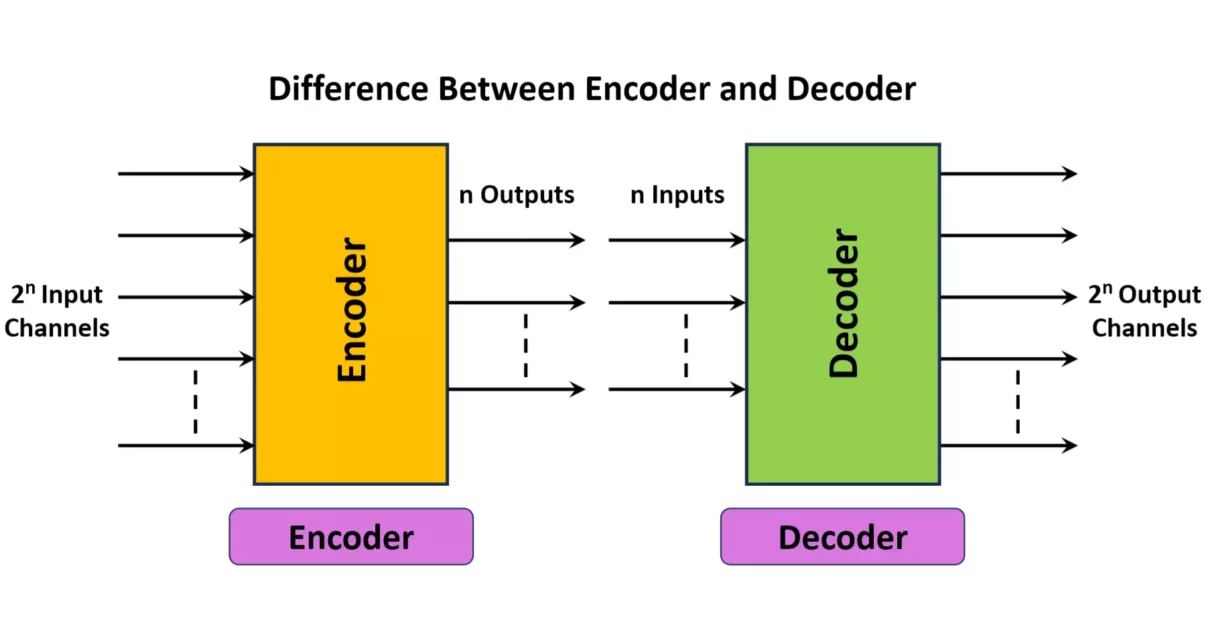
Difference Between Encoder and Decoder with Applications
While they may seem like two sides of the same coin, encoders and decoders serve opposite but equally crucial roles. In this article, we’ll learn about difference between encoder and decoder with their types, pros and cons, real-world applications, and some of the most commonly used encoder and decoder ICs. In the world of digital […]
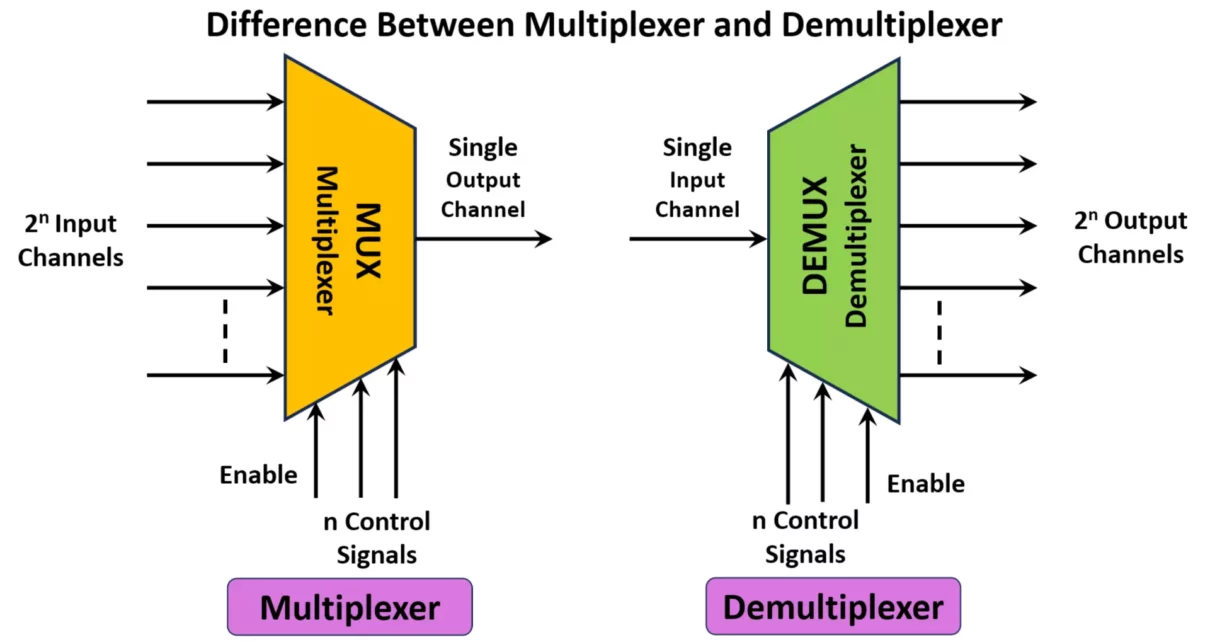
Difference Between Multiplexer and Demultiplexer with Types
Multiplexers (MUX) and Demultiplexers (DEMUX) are essential combinational logic circuits used in digital electronics for data transmission and communication systems. They play a crucial role in efficiently handling multiple signals by optimizing the usage of data lines, reducing hardware complexity, and enhancing the efficiency of data processing units. Let’s explore the difference between multiplexer and […]
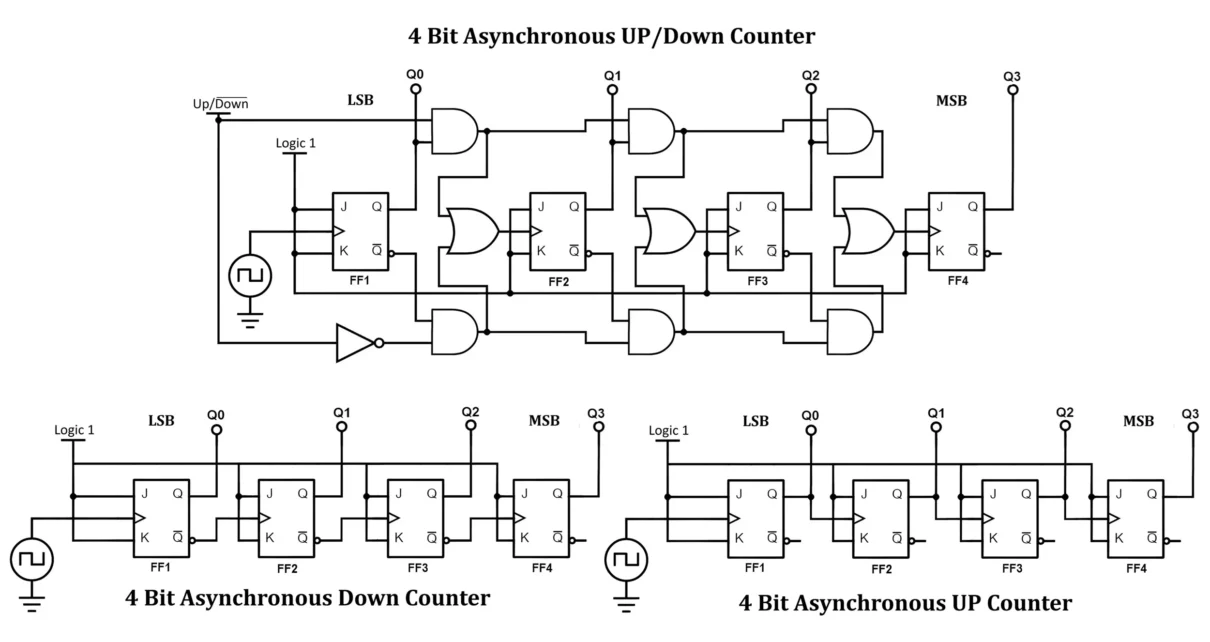
4 Bit Asynchronous Counters: Working and Applications
An Asynchronous Counter, also known as a Ripple Counter, is a type of digital counter where the clock signal is applied to only the first flip-flop, and subsequent flip-flops toggle based on the output of the previous one. This introduces a propagation delay, making it “asynchronous.” Asynchronous Binary Counter Terminology Here’s a breakdown of all […]