The Diac is basically a two-terminal device. Here we will discuss the symbol, construction, VI characteristics, advantages, disadvantages and applications of Diac. It is such a combination of semiconductor layers that allows triggering in both directions. The Diac is used as a triggering device for the TRIAC circuits.
What is a DIAC?
A DIAC (Diode for Alternating Current) is a bilateral semiconductor switch that can conduct current in both directions once its breakover voltage is exceeded. DIACs don’t conduct until a certain threshold, and after reaching this voltage, they switch on and allow current to pass.
Symbol and Construction of DIAC:
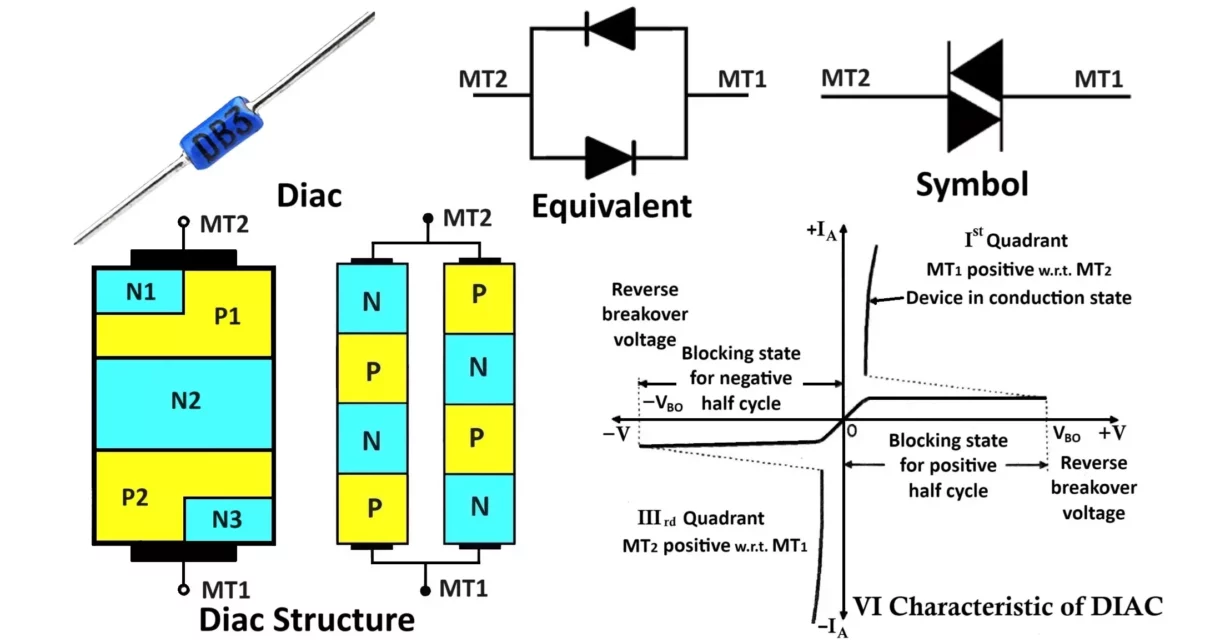
The arrangement of a semiconductor layer is as shown in Figure. The two terminals accessible to the user are MT1 and MT2.
When MT2 is positive with respect to MT1 the conduction takes place through the structure formed by the layers p1-n2-p2-n3.
Similarly, when MT1 is positive with respect to MT2 the conduction takes place through the structure formed by the p2-n2-p1-n1 layers. Therefore, the equivalent circuit of Diac is like two diodes connected back-to-back.
structurally it’s a one PNPN device, not two separate diodes. It conducts after reaching its breakover voltage in either polarity not like an ordinary diode that conducts immediately.
The figure shows the circuit symbols for the Diac. Indicating that the Diac can conduct in both directions. The symbol of Diac is identical to that of a Triac without a gate terminal.
VI Characteristics of DIAC:
- The static characteristic of Diac is as shown in graph We may think of Diac being equivalent to a bipolar transistor with no base connection.
- Diac can be turned on by either a positive or negative half cycle of an ac voltage. For the positive cycle of ac voltage, if the applied voltage is less than the forward breakover voltage a very small current called the “leakage current'”, flows through the device.
- This current is produced due to the drifting of electrons and the holes at the depletion region and is not sufficient to cause conduction.
- Hence the Diac remains in the non-conducting mode called the “blocking state” or off state.
- As soon as the applied voltage reaches the breakover voltage, (Vbo) the device starts conducting. The current through the device starts increasing and the voltage across it starts decreasing.
- This region is the “conduction state”. There is no control over the breakover voltage for the Diac remains unchanged as the gate terminal is absent here. The characteristics of the Diac are very much similar to that of a Triac.
- For the positive half cycle of the ac supply, the characteristic is obtained in the first quadrant and a similar characteristic for the negative half cycle is obtained in the third quadrant as shown in Figure.
- The breakover voltage of a Diac ranges between 28 Volts to 42 Volts. The typical turn-on time ranges from 50 to 500 nsec.
- The turn off time is much longer, about 100 nsec. Diacs have a power handling capacity between 300 mW to 1W which shows that it is a low power device.
Advantages of DIAC:
- Simplicity & Low Cost – Its structure is straightforward and inexpensive.
- Bilateral Conduction – Can trigger equally on both AC polarities.
- Reliable Triggering – Sharp, stable breakover voltage for accurate triggering.
- Compact Size – Requires very little space on a circuit board.
- Long Life – Solid-state device with long operational life and high mean time between failures.
Disadvantages of DIAC:
- No Gate Control – Unlike a TRIAC or SCR, the DIAC cannot be externally triggered.
- Limited Power Rating – Suited for low-power triggering only.
- Breakover Voltage Spread – Breakover voltages have a tolerance range and can vary between devices.
- Low Switching Speed – Suitable for power control but not for very high-speed switching.
Applications of DIAC:
- Triggering Device for TRIACs – Commonly used in light dimmers, fan speed controllers, and heat control circuits.
- Phase Control Circuits – Provides symmetrical triggering of TRIACs.
- Lamp Dimmers – Controls intensity of incandescent lamps.
- Motor Speed Control – Used in small AC motor control circuits.
- Over-Voltage Protection Circuits – Protects against transient spikes by conducting when a threshold is reached.
Summary
| Factor | DIAC |
|---|---|
| Advantages | Simple, inexpensive, bilateral, long life |
| Disadvantages | No gate control, limited power, fixed breakover |
| Applications | TRIAC triggering, light dimmers, speed control |
Some of the very popular Diac are DB3, DB4, DB5, BR100, ER900 and DB6.
Conclusion:
A DIAC conducts current in both directions once the applied voltage exceeds its breakover point. This bilateral, two-terminal, four-layer semiconductor switch commonly triggers TRIACs in AC power control circuits, such as light dimmers and speed controllers, and provides smooth, symmetrical switching with simple, reliable operation.
What is Thyristor? Working, Symbol, Construction, Types, Operation, Protection and Applications