A fusible resistor is a safety resistor designed to do two jobs at once: limit current and act like a fuse. Under normal conditions it behaves like a regular resistor, but if too much current flows, it overheats and safely opens the circuit, preventing damage or fire.
You’ll often find fusible resistors in power supplies, TVs, amplifiers, and other electronics where protecting the circuit is critical. Unlike ordinary resistors that may burn, char, or fail unpredictably, fusible resistors are engineered to open the circuit cleanly when excessive current flows, similar to a fuse, hence the name fusible resistor.

Fusible Resistor Symbol
A fusible resistor uses the standard resistor symbol, but in schematics it is often: marked with “FR” or annotated with “Fusible” Sometimes drawn with a small fuse-style break or diagonal line
Important Note:
Electrically, it behaves like a resistor until its rated power or current is exceeded.
Related Articles:
- Wire Wound Resistor Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Carbon Composition Resistor Construction, Working & Applications
- Carbon Film Resistor Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Metal Film Resistor Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Metal Oxide Resistor Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Types of Resistors with Symbol, Classification and Applications
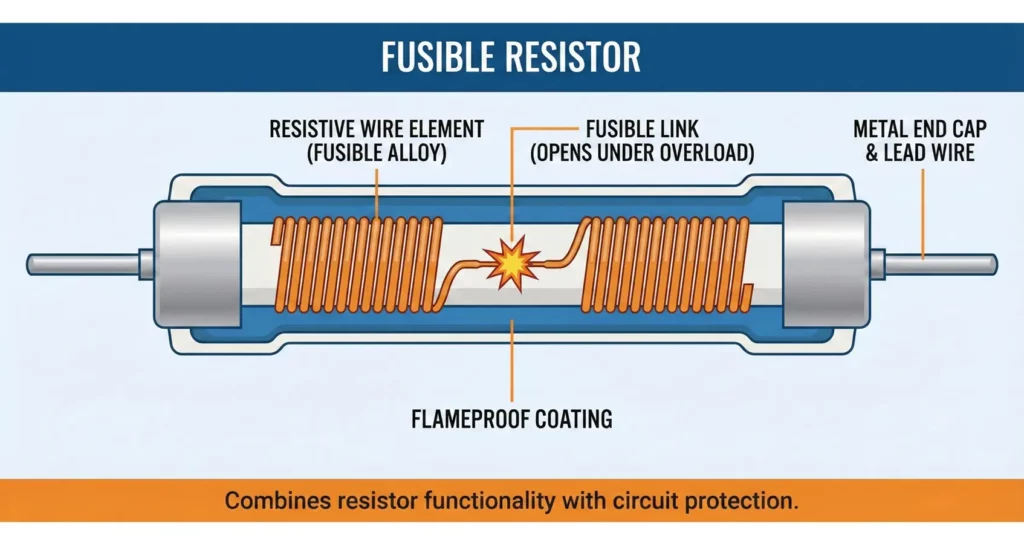
Construction of Fusible Resistor
The construction of a fusible resistor is fundamentally different from standard carbon or metal film resistors to ensure controlled failure.
Key Construction Elements
- Resistive Element
- Made from metal alloy or metal oxide film
- Precisely engineered to melt at a defined energy level
- Acts as both resistance path and fuse element
- Ceramic Core
- High-temperature ceramic rod
- Maintains mechanical stability under thermal stress
- Flameproof Coating
- Special non-flammable cement or epoxy
- Prevents fire, sparks, or molten metal spray
- End Caps and Leads
- Nickel-plated or tinned copper
- Designed to withstand brief overloads without detaching
- Controlled Weak Point
- Thinner resistive section ensures predictable fusing behavior
Working Principle of Fusible Resistor
The operation of a fusible resistor is based on Joule heating (I²R loss).
Normal Operation
- Current flows within rated limits
- Resistor functions like a standard resistor
- Heat dissipation remains below failure threshold
Fault Condition (Overcurrent / Short Circuit)
- Current rises sharply
- Power dissipation increases exponentially
- Resistive element heats rapidly
- Element melts and opens the circuit
- No flame, no explosion, no conductive residue
After Failure
- Circuit remains permanently open
- Prevents downstream damage
- Eliminates risk of fire or PCB carbonization
Electrical Characteristics
- Resistance Range: Typically, 0.1 Ω to 100 Ω and some variants extend into kilo-ohm range
- Power Rating: Common ratings are 0.25 W, 0.5 W, 1 W, 2 W. Must be derated for temperature
- Tolerance: ±5%, ±10%
- Temperature Coefficient: Moderate (higher than precision metal film resistors)
- Fusing Time: Depends on overcurrent magnitude, ambient temperature, physical size of element.
How to Read Fusible Resistor Value
Fusible resistors usually follow color coding or alphanumeric marking, depending on package type.
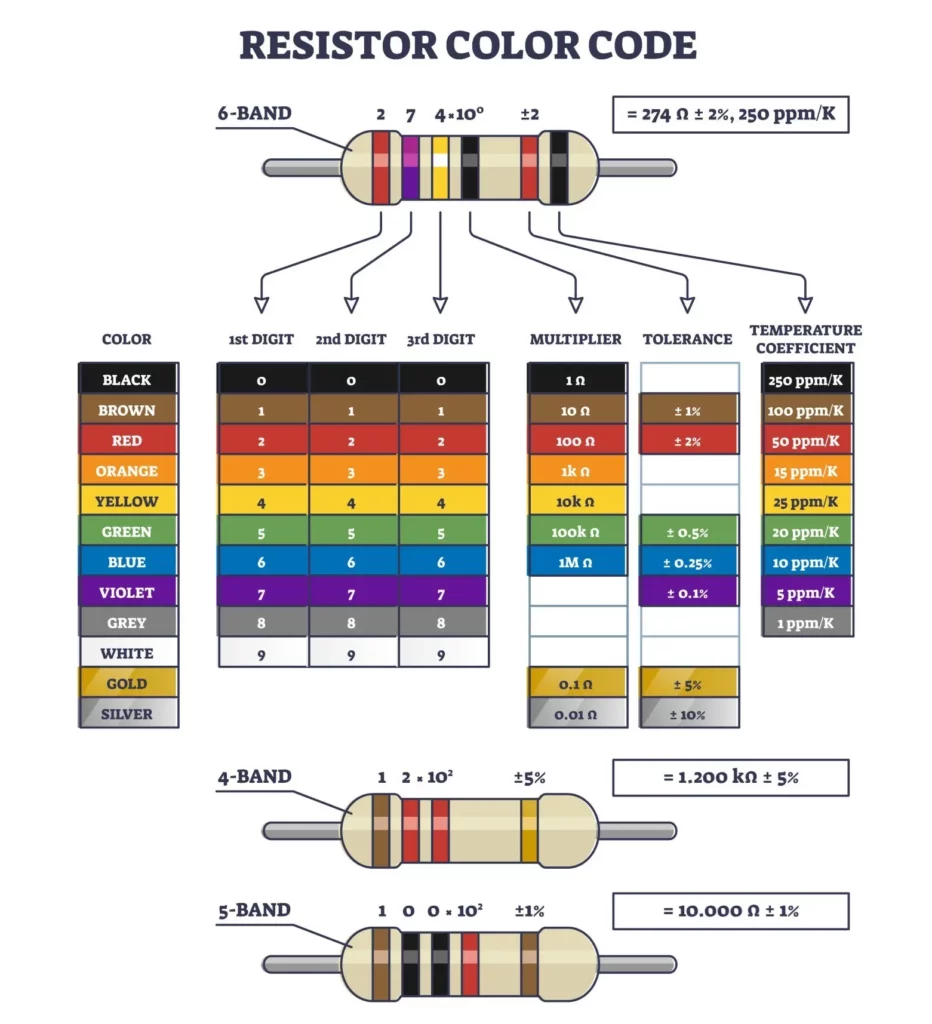
Color Code Method
Same as standard resistor code:
- 4-band or 5-band color system
- Last band indicates tolerance
Printed Markings
- Low-value fusible resistors may use: “0R22” → 0.22 Ω and “1R0” → 1 Ω
- Often accompanied by: FR, F Manufacturer-specific code
Always confirm Fusible rating, Flameproof compliance, Interrupting capacity with datasheet
Types of Fusible Resistors
- Wire-wound Fusible Resistor
- Uses fine resistance wire
- High surge tolerance
- Common in power supplies
- Metal Film Fusible Resistor
- Thin metal film with weak section
- Faster fusing action
- Compact size
- Metal Oxide Fusible Resistor
- Excellent thermal stability
- High temperature endurance
- Common in SMPS input stages
- Cement-Type Fusible Resistor
- Encased in ceramic cement block
- High power ratings
- Often used as current sense + fuse
Selection Criteria
Selecting a fusible resistor requires both resistor design rules and fuse safety rules. Here are the key parameters to consider:
- Resistance Value: Must meet circuit current and voltage requirements
- Power Rating: Choose ≥2× normal operating power
- Fusing Characteristic
- Fast-blow or slow-blow behavior
- Depends on surge current profile
- Voltage Rating: Ensure safe interruption without arcing
- Flameproof Certification: UL94 V-0 or equivalent
- Ambient Temperature: Apply derating curves
- PCB Spacing: Maintain clearance for safety isolation
Advantages of Fusible Resistor
- Combines resistor + fuse in one component
- Saves PCB space and cost
- Predictable and safe failure mode
- No flame or explosion
- Protects semiconductors and transformers
- Ideal for unattended equipment
Disadvantages of Fusible Resistor
- One-time protection only
- Not suitable for frequent overload events
- Limited resistance range compared to standard resistors
- Replacement required after fault
- Slower response than semiconductor protection devices
Applications of Fusible Resistors
Fusible resistors are widely used where safety and reliability are critical.
- SMPS primary input stages
- Linear power supplies
- Battery chargers
- CRT and LCD TVs
- Audio amplifiers
- Industrial control circuits
- Consumer electronics
- Inrush current limiting
- Short-circuit protection
Fusible Resistor vs Fuse
| Parameter | Fusible Resistor | Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Has resistance | Nearly zero |
| Normal function | Limits current | Does nothing |
| Failure mode | Clean open | Clean open |
| Cost | Low | Low |
| Replacement | After fault | After fault |
Summary Table
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Current limiting + circuit protection |
| Construction | Metal film / oxide on ceramic core |
| Failure Mode | Controlled open circuit |
| Power Rating | 0.25 W to several watts |
| Resistance Range | Sub-ohm to kilo-ohm |
| Safety | Flameproof, non-explosive |
| Applications | SMPS, chargers, TVs, amplifiers |
Conclusion
A fusible resistor is far more than a simple resistor; it is a critical safety component designed to protect electronic systems from catastrophic failure. By combining resistance and fusing action in a single, flameproof package, it ensures predictable behavior under fault conditions, making it indispensable in modern power electronics and consumer devices.
For safe and robust circuit design, understanding and correctly selecting fusible resistors is not optional, it is essential.
Types of Resistors with Symbol, Classification and Applications
Wire Wound Resistor Construction, Working, Types and Applications
Metal Oxide Resistor Construction, Working, Types and Applications